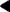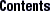Creating or Changing a Rights Profile
To create or change a rights profile, you must either assume a role that has the Primary Administrator rights profile assigned to it, or run the User Tool Collection as root user if roles have not yet been set up. To learn more about rights profiles, see "RBAC Roles" and "Configuring Recommended Roles".
 How to Create or Change a Rights Profile by Using the Rights Tool
How to Create or Change a Rights Profile by Using the Rights Tool
Start the Rights tool.
To run the Rights tool, you need to start the Solaris Management Console as described in "How to Assume a Role in the Console Tools". Then, open the User Tool Collection, and click the Rights icon.
After the Rights tool starts, the icons for the existing rights profiles are displayed in the view pane.
Take the appropriate action for creating or changing a rights profile:
To create a new rights profile, select Add Right from the Action menu.
To change an existing rights profile, click the rights profile icon and select Properties from the Action menu (or simply double-click the rights profile icon).
Both actions display a version of the Rights Properties dialog box. The Add Right version (which follows) has a writable Name field. The standard Rights Properties dialog box has a read-only Name field because the name of a rights profile cannot be changed after it has been defined.
Figure 18-5 Add Right Dialog Box
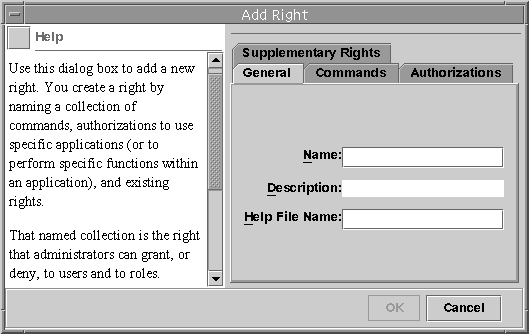
Type the new information. Click OK to save the rights profile.
The following table lists the tabs and fields in the Right Properties dialog box.
Tab
Field
Field Description
General
Name
Name of the new rights profile.
Description
Description of the new rights profile.
Help File Name
Name of the HTML help file for the new rights profile.
Commands
Add Directory
Opens a dialog box for adding directories that are not already in the Commands Denied or Commands Permitted columns.
Commands Denied / Commands Permitted
Assigns or removes a rights profile's commands.
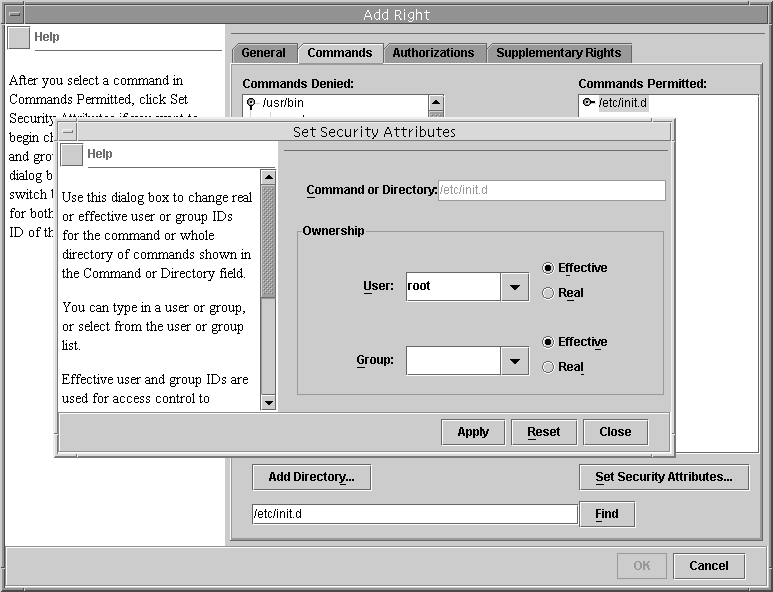
Opens a dialog box for assigning or removing a command's security attributes, that is, real or effective UIDs or GIDs (see Figure 18-6).
Note -
Assigning effective IDs is preferred over assigning real IDs. Use real IDs only when they are required by the command, such as pkgadd.
Find (command)
Searches the two command lists for the specified string.
Authorizations
Authorizations Excluded / Authorizations Included
Assigns or removes a rights profile's authorizations.
Supplementary Rights
Rights Excluded / Rights Included
Assigns or removes a rights profile's supplementary rights profiles.
Figure 18-6 Adding Security Attributes to Commands
Example 18-2 Creating a New Rights Profile With the Rights Tool
The data in the following table shows sample data for a hypothetical rights profile that is called "Restart" could be created. The example rights profile, Restart, has the commands in the subdirectory /etc/init.d assigned to it. These commands have an effective UID of 0. This rights profile would be useful for administrators who are permitted to stop and start the daemons in /etc/init.d.
Tab | Field | Example |
|---|---|---|
General | Name | Restart |
| Description | For starting and stopping daemons in /etc/init.d |
| Help File Name | Restart.html |
Commands | Add Directory | Click Add Directory, type /etc/init.d in the dialog box, and click OK. |
| Commands Denied / Commands Permitted | Select /etc/init.d and click Add to move the command to the Commands Permitted column. |
| Set Security Attributes | Select /etc/init.d, click Set Security Attributes, and set Effective UID = root (see Figure 18-6). |
| Find (command) |
|
Authorizations | Authorizations Excluded / Authorizations Included |
|
Supplementary Rights | Rights Excluded / Rights Included |
|
 How to Change Rights Profiles From the Command Line
How to Change Rights Profiles From the Command Line
Become superuser or assume a role with the PrimaryAdministration rights profile.
Use the subcommand of smprofile that is appropriate for the task.
This command requires authentication. You can apply the command to all name services. smprofile runs as a client of the Solaris Management Console server.
To add a new profile, use smprofile with the add subcommand.
To change an existing profile, use smprofile with the modify subcommand.
Modifying a User's RBAC Properties
To modify a user's properties, you must either be running the User Tool Collection as root user or assume a role that has the Primary Administrator rights profile assigned to it.
 How to Modify a User's RBAC Properties by Using the User Accounts Tool
How to Modify a User's RBAC Properties by Using the User Accounts Tool
Start the User Accounts tool.
To run the User Accounts tool, you need to start the Solaris Management Console, as described in "How to Assume a Role in the Console Tools". Then, open the User Tool Collection, and click the User Accounts icon.
After the User Accounts tool starts, the icons for the existing user accounts are displayed in the view pane.
Click the user account icon to be changed and select Properties from the Action menu (or simply double-click the user account icon).
Click the appropriate tab in the dialog box for the property to be changed, as follows:
To change the roles that are assigned to the user, click the Roles tab and move the role assignment to be changed to the appropriate column: Available Roles or Assigned Roles.
To change the rights profiles that are assigned to the user, click the Rights tab and move it to the appropriate column: Available Rights or Assigned Rights.
Note - It is not good practice to assign rights profiles directly to users. The preferred approach is to force users to assume roles in order to perform privileged applications. This strategy avoids the possibility of normal users abusing privileges.
 How to Modify a User's RBAC Properties From the Command Line
How to Modify a User's RBAC Properties From the Command Line
Become superuser or assume a role that can modify user files.
Use the appropriate command:
To change the authorizations, roles, or rights profiles that are assigned to a user who is defined in the local scope, use the usermod command.
Alternatively, to change the authorizations, roles, or rights profiles that are assigned to a user who is defined in the local scope, edit the user_attr file.
This method is recommended for emergencies only, as it is easy to make a mistake while you are typing.
To change the authorizations, roles, or rights profiles that are assigned to a user who is defined in a name service, use the smuser command.
This command requires authentication as superuser or as a role that is capable of changing user files. You can apply smuser to all name services. smuser runs as a client of the Solaris Management Console server.